F21c was submitted to Mosis for fabrication on 6/4/97.
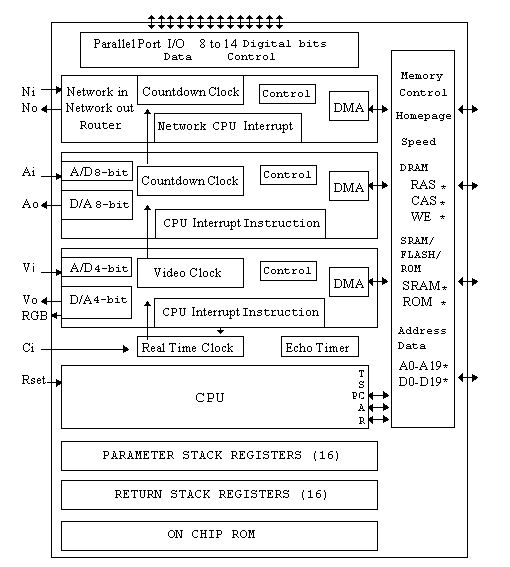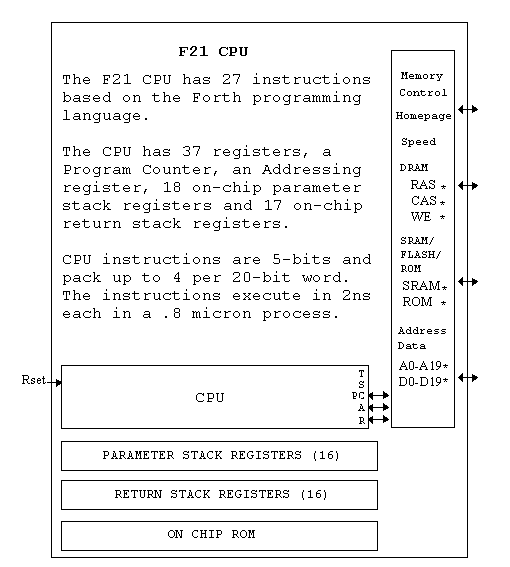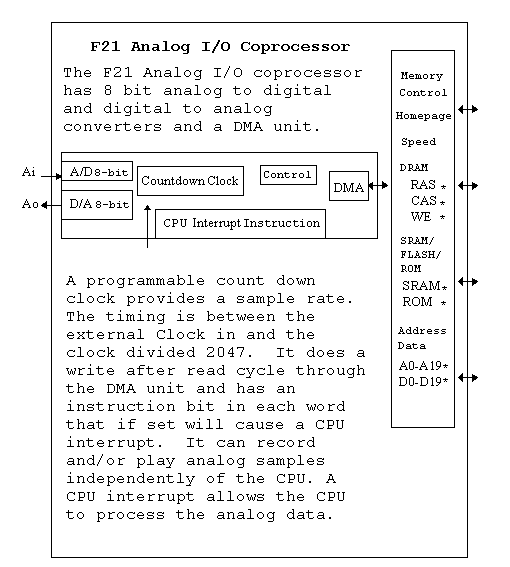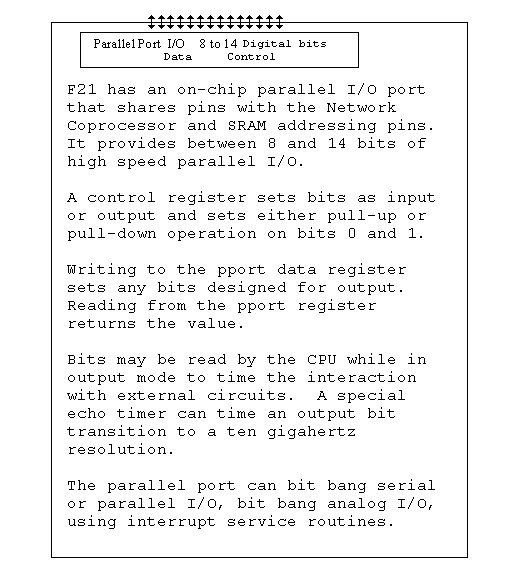
The F21 microprocessor contains a Stack Machine CPU, a video i/o coprocessor, an analog i/o coprocessor, a serial network i/o coprocessor, an parallel port, a real time clock, some on chip ROM, and an external memory interface.
F21 is being fabricated .8 micron CMOS technology using the HP process at Mosis. F21 is being prototyped in a 68 pin ceramic package similar to the 68 pin PLCC that will be used for production. Click here to see the die size and chip pinouts and current F21 status, or click here to see the current F21c prototype Printed Circuit Board.
It will access to 3 memory spaces, one megaword of 20 bit wide DRAM, 8K words of 20 bit wide fast SRAM, and one megabyte of 8 bit wide PROM, SRAM, FRAM, or PCMCIA CARD memory for booting. It will interface directly to 5 1Mx4 or 265Kx4 DRAMS and/or 3 8Kx8 high speed SRAM. A system can be built with only 5 or 7 chips. Memory timing for the three memory spaces are: 150ns or 250ns for 8 bit SRAM, 40ns onpage and 140ns offpage 20 bit DRAM, and 12ns or 25ns for 20 bit fast SRAM. All memory timings are adjustable within a 40% speedup range. The interal ROM has an 8ns setup and 4ns load time for a total access time of 12ns. The chip also provides a parallel I/O port decoded and latched on chip.
The memory interface processor provides memory access to all processors giving lowest priority to the CPU. The I/O coprocessors can be turned on or off by the CPU, and can run continuously executing their own instructions, or can interrupt the CPU to process their data buffers or instructions.

Updated 6/1/97
F21C prototype submission is planned for this week. F21C will be the third F21 prototype design prepared by Chuck Moore and submited for fabrication by MOSIS in .8 micron CMOS. F21C will be packaged in a 68 pin plcc package similar to the production part.
Ultra Technology Inc. will offer a development board and software for the F21C when the chips are being tested. A small quantity of prototyp chips may be available at that time testing. The yield, cost, and availability will be know after testing.
The F21c has pinout and control register changes from the F21b prototype which was packaged in a 65 pin PGA.
F21b had 3 power and 3 ground pins as did early i21 chips. F21c will have 6 power and 6 ground pins. This may be more than needed and a production part may replace some of these power and ground pins with other functions.
As with F21b F21c will not have composite video out or video input functionality. On F21b the pins were there but the circuits were not functional. On F21c there are no Vo and Vi pins. The video coprocessor on this prototype has RGB output only.
There have also been changes to the parallel port on F21c. The extra SRAM addressing lines and serial/network pins are also mapped to parallel port lines so that they can be used as parallel port i/o bits if they not being used for SRAM addressing or serial networking. It will also permit the Serial Out line to be tri-stated to support multiple network topologies.
There is also one more SRAM addressing bit A13 on P13. This allows for direct addressing of 16K words of high speed 20 bit wide SRAM to take full advantage of the 16K word sized Home Page addressing feature.
One will also notice that the die size and scale of the chip have changed. F21b had 64 pads and was twice as high as it was wide. The F21c die has 68 pads and is nearly square. F21b used .8 micron, but used larger tile sizes than F21c so the actual F21c is smaller and has more unused area on the die.